
Stellar Shine
Drone Cleaning in Space
Dust accumulation is a significant obstacle for solar-powered systems on Mars and Earth alike. On Mars, the atmosphere gradually coats solar panels in dust, reducing their efficiency and threatening mission success. This same challenge affects solar farms in arid regions on Earth, where energy production can drop by up to 30% within a month if panels are not cleaned regularly.
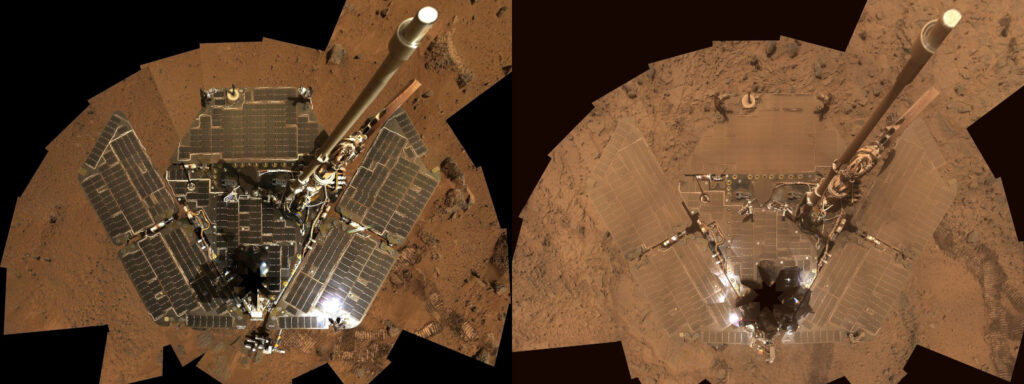
AIr™‘s autonomous drone airflow cleaning technology addresses dust accumulation without physical contact or water — making it ideal for both terrestrial and extraterrestrial environments. (photo: NASA/JPL-Caltech)
Lessons from NASA’s Rovers
NASA’s rovers have provided invaluable data about Mars since 2004, but dust accumulation has consistently threatened their operational lifespans:
- Spirit (2004–2010): Ceased operations when its solar panels became irreversibly covered in dust.
- Opportunity (2004–2019): Survived for nearly 15 years but ultimately succumbed to unprecedented Martian dust storms that coated its panels.
- Sojourner (1997): Saw its power output reduced by 23% during a 90-day mission due to dust accumulation.
While Martian winds occasionally clear dust from solar panels, they also contribute to re-soiling during subsequent storms—an unpredictable cycle that limits the efficiency of solar-powered systems.
Manual cleaning methods are prone to human error—fatigue, carelessness, or using water at the wrong temperature can cause micro-cracks in panel glass. In contrast, drones clean panels safely and consistently without physical contact or water.
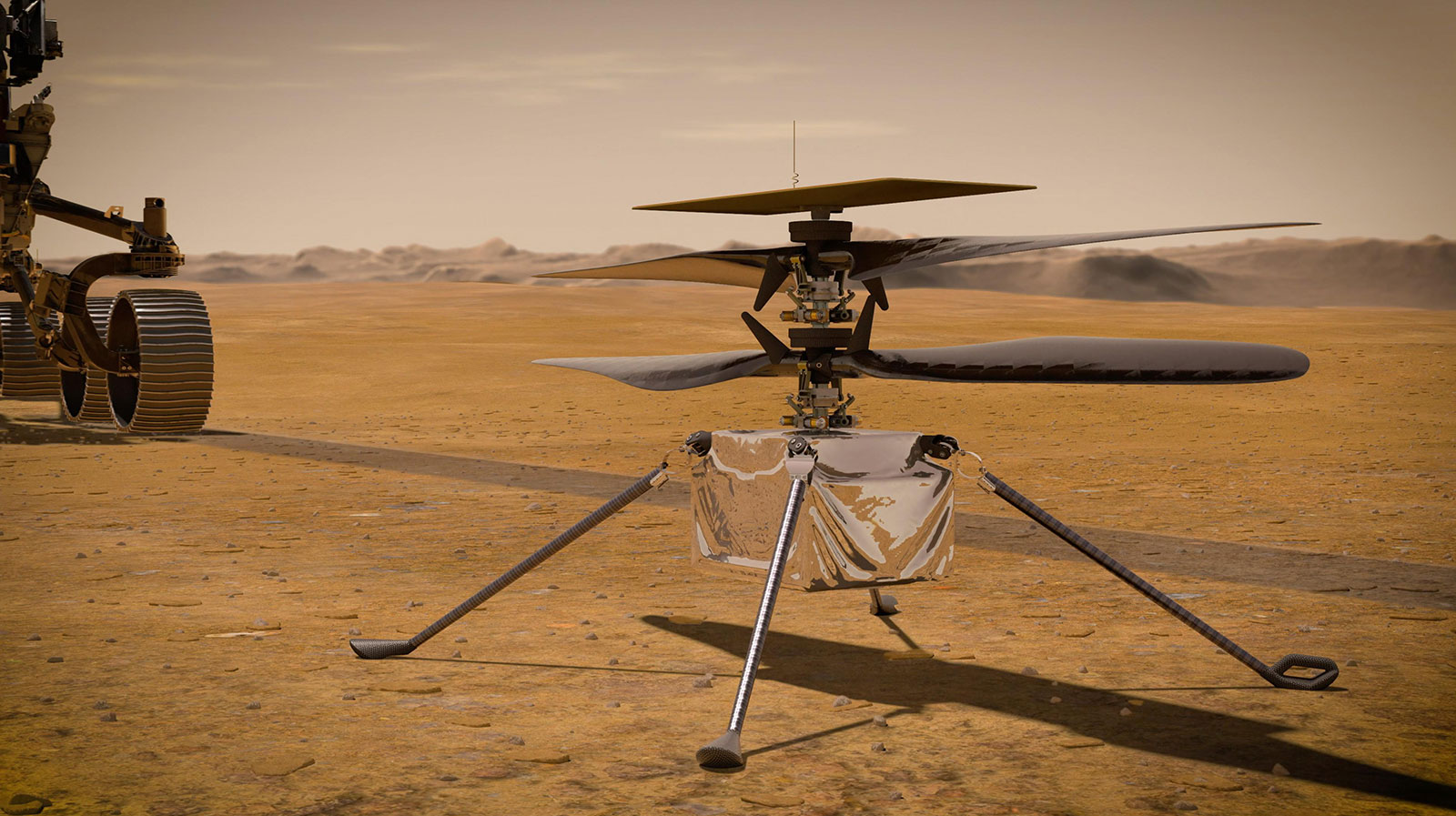
Ingenuity: A New Era of Exploration
NASA’s latest rover, Perseverance, landed on Mars in February 2021 with a groundbreaking addition: the helicopter Ingenuity. Powered by solar cells, Ingenuity represents the first aerial exploration vehicle deployed on another planet. Its success highlights the potential for autonomous aerial systems to address challenges like dust accumulation in extreme environments.
Lessons from NASA’s Rovers
NASA’s rovers have provided invaluable data about Mars since 2004, but dust accuHow AIr™ Technology Could Advance Future Space Missions
Dust accumulation on Mars is a persistent challenge for long-term missions reliant on solar power. While current solutions rely on passive methods like angling panels to catch surface winds, future missions could benefit from active cleaning systems like AIr™ drones.
Applications in Space Exploration:
- Solar Panel Cleaning for Rovers:
AIr™ drones could autonomously clean solar panels on rovers, ensuring consistent energy output during long-term missions and reducing reliance on unpredictable Martian winds. - Maintenance of Stationary Solar Arrays:
Future Mars colonies or research stations will likely use stationary solar farms for power generation. AIr™ drones could provide regular cleaning without requiring manual intervention or water-based methods. - Dust Management for Sensitive Equipment:
Beyond solar panels, AIr™ drones could clean sensors, cameras, and other critical equipment exposed to Martian dust storms—maintaining functionality and extending mission lifespans. - Adaptability Across Environments:
AIr™ drones are lightweight and non-tactile, making them ideal for deployment in low-gravity environments like Mars or the Moon.

Bringing “Cleaning Events” to Earth
Inspired by Martian challenges, AIr™ has developed autonomous drone cleaning technology that mimics the “cleaning events” caused by Martian winds. These drones use precise downward airflow generated by their rotors to blow away dust and debris from solar panels — row by row — without physical contact or water.
This technology is particularly impactful in sun-rich, arid regions where cleaning costs are high due to logistical challenges. By providing frequent, waterless cleaning solutions, AIr™ drones reduce operational costs while increasing energy output and profitability for solar farms.
A Mission for Sustainability
“Our mission is to reduce operation and maintenance costs for solar energy while increasing panel profitability,” said inventor Ridha Azaiz. “By using our innovative drone cleaning technology, we aim to decrease the frequency of manual wet cleans, making solar energy more accessible and efficient — even in marginal areas.”
AIr™ technology bridges the gap between space exploration and terrestrial sustainability by addressing one of the most pressing challenges faced by both Martian missions and Earth-based solar farms: dust accumulation. AIr™ exemplifies how innovation can drive progress in renewable energy while solving real-world challenges here on Earth and beyond.
